In today’s complex cybersecurity landscape, businesses are constantly facing evolving threats. Traditional security measures often fall short in detecting sophisticated attacks that can bypass firewalls and antivirus software. That’s where Remote Monitoring and Management (RMM) analytics come into play, offering a proactive approach to identifying and mitigating potential security breaches.
RMM tools, primarily designed for managing and maintaining IT infrastructure remotely, generate a wealth of data. This data, when analyzed effectively, can provide valuable insights into system behavior, network activity, and user patterns. By leveraging the power of RMM analytics, IT professionals can detect anomalies, identify suspicious activities, and respond to threats before they cause significant damage.

This article delves into the world of cybersecurity threat detection through RMM analytics. We’ll explore how RMM tools can be used to enhance security posture, the key features and functionalities that enable threat detection, and the challenges and best practices associated with implementing RMM-based security solutions. Whether you’re a seasoned IT professional or just starting to explore the possibilities of RMM, this guide will provide you with a comprehensive understanding of how to leverage RMM analytics for improved cybersecurity.
Understanding RMM and its Role in Cybersecurity
Remote Monitoring and Management (RMM) is a software solution used by IT service providers (MSPs) and internal IT departments to remotely monitor and manage client endpoints, networks, and systems. It allows for proactive maintenance, patch management, software deployment, and remote troubleshooting. While primarily used for operational efficiency, RMM tools have become increasingly valuable for cybersecurity.
Key Features of RMM Tools
RMM tools typically include the following features:
- Remote Access: Allows IT professionals to access and control remote devices for troubleshooting and maintenance.
- Monitoring: Continuously monitors system performance, network health, and security events.
- Patch Management: Automates the process of deploying security patches and software updates.
- Automation: Enables automated tasks such as script execution, software installation, and system restarts.
- Reporting: Generates reports on system performance, security events, and other relevant metrics.
- Alerting: Sends notifications when predefined thresholds are exceeded or critical events occur.
How RMM Data Enhances Cybersecurity
The data collected by RMM tools provides a comprehensive view of the IT environment. This data can be analyzed to identify:
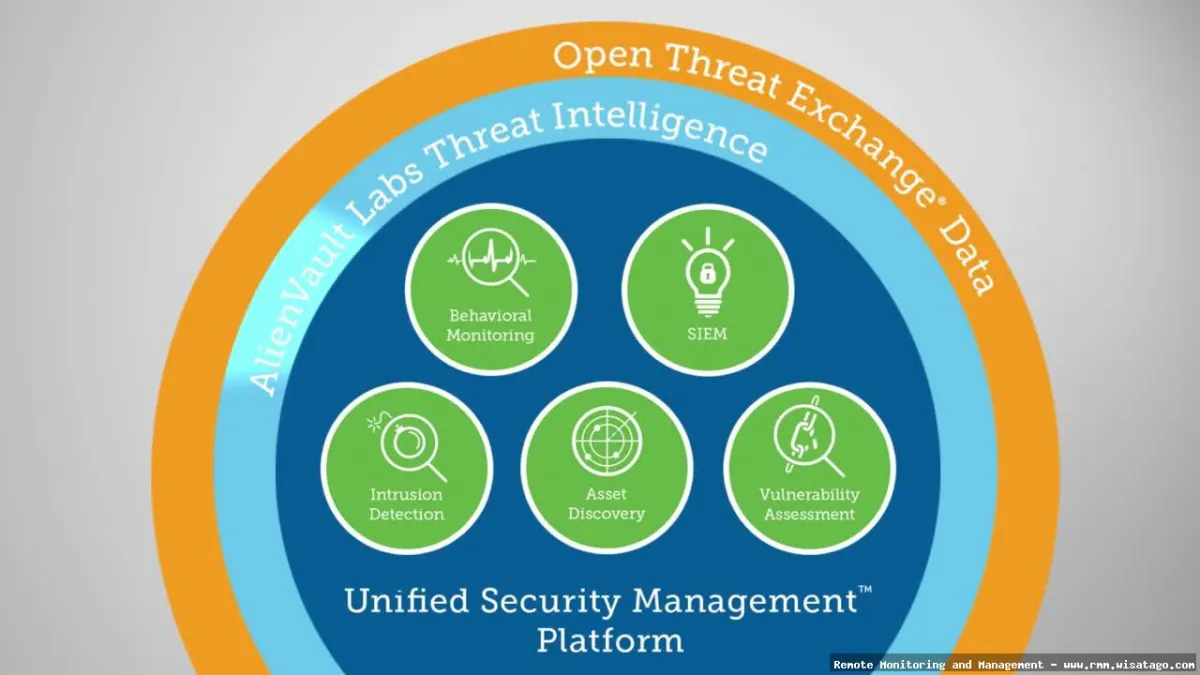
- Anomalous Behavior: Deviations from normal system or user behavior that could indicate a security threat.
- Vulnerabilities: Unpatched systems, outdated software, and misconfigured settings that could be exploited by attackers.
- Malicious Activity: Suspicious processes, network connections, and file modifications that could indicate malware infection.
- Policy Violations: Users violating security policies, such as accessing unauthorized websites or downloading prohibited software.
Cybersecurity Threat Detection with RMM Analytics
RMM analytics involves analyzing the data collected by RMM tools to identify and respond to cybersecurity threats. This requires a combination of technical expertise, advanced analytics tools, and a proactive approach to security.
Identifying Anomalous Behavior
One of the most effective ways to detect threats with RMM analytics is to identify anomalous behavior. This involves establishing a baseline of normal system and user activity and then looking for deviations from that baseline. For example:
- Unusual Login Activity: Detecting logins from unfamiliar locations or at unusual times.
- Spikes in Network Traffic: Identifying sudden increases in network traffic that could indicate a denial-of-service (DoS) attack or malware infection.
- Unexpected Process Execution: Detecting the execution of processes that are not normally run on a system.
- File Modification Anomalies: Identifying unauthorized modifications to critical system files.
Detecting Vulnerabilities
RMM tools can also be used to detect vulnerabilities that could be exploited by attackers. This includes:
- Unpatched Systems: Identifying systems that are missing critical security patches.
- Outdated Software: Detecting software that is vulnerable to known exploits.
- Misconfigured Settings: Identifying systems with insecure configurations, such as weak passwords or open ports.
Analyzing Logs and Events
RMM tools collect a vast amount of log data from various sources, including system logs, application logs, and security logs. This data can be analyzed to identify suspicious events and patterns. For example:

- Failed Login Attempts: Identifying brute-force attacks by monitoring failed login attempts.
- Security Alerts: Analyzing security alerts generated by firewalls, intrusion detection systems, and antivirus software.
- System Errors: Investigating system errors that could indicate a security problem.
Leveraging Threat Intelligence
RMM analytics can be enhanced by integrating with threat intelligence feeds. These feeds provide up-to-date information on known threats, vulnerabilities, and attack patterns. By correlating RMM data with threat intelligence data, IT professionals can more quickly identify and respond to emerging threats.
Implementing RMM Analytics for Cybersecurity
Implementing RMM analytics for cybersecurity requires careful planning and execution. Here are some key steps to consider:
Choosing the Right RMM Tool
Not all RMM tools are created equal. When choosing an RMM tool for cybersecurity, consider the following factors:
- Security Features: Look for RMM tools that offer built-in security features, such as vulnerability scanning, intrusion detection, and behavioral analysis.
- Integration Capabilities: Choose an RMM tool that integrates with other security tools, such as SIEM systems, threat intelligence platforms, and antivirus software.
- Reporting and Analytics: Ensure that the RMM tool provides robust reporting and analytics capabilities.
- Scalability: Select an RMM tool that can scale to meet the needs of your organization as it grows.
Configuring RMM for Security Monitoring
Once you’ve chosen an RMM tool, you need to configure it for security monitoring. This involves:

. Effective IT management often involves a suite of tools, where RMM plays a key role in proactive monitoring and maintenance
.
- Defining Monitoring Policies: Establishing clear policies for monitoring system performance, network activity, and security events.
- Setting Thresholds and Alerts: Configuring alerts to be triggered when predefined thresholds are exceeded or critical events occur.
- Enabling Logging: Ensuring that all relevant logs are being collected and stored.
- Implementing Security Hardening: Applying security hardening measures to protect the RMM tool itself from attack.
Analyzing RMM Data
Analyzing RMM data requires a combination of technical expertise and the right tools. You may need to use:
- SIEM Systems: Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) systems can aggregate and analyze log data from multiple sources, including RMM tools.
- Security Analytics Platforms: Security analytics platforms provide advanced analytics capabilities, such as machine learning and behavioral analysis.
- Manual Analysis: In some cases, manual analysis of RMM data may be necessary to investigate suspicious events.
Responding to Threats
When a threat is detected, it’s important to respond quickly and effectively. This may involve:
- Isolating Infected Systems: Disconnecting infected systems from the network to prevent the spread of malware.
- Removing Malware: Using antivirus software or other tools to remove malware from infected systems.
- Patching Vulnerabilities: Applying security patches to address vulnerabilities that were exploited by attackers.
- Investigating the Incident: Conducting a thorough investigation to determine the root cause of the incident and prevent future attacks.
Challenges and Best Practices
Implementing RMM analytics for cybersecurity can be challenging. Here are some common challenges and best practices to consider:
Challenges
- Data Overload: RMM tools generate a vast amount of data, which can be overwhelming to analyze.
- False Positives: RMM analytics can generate false positives, which can waste time and resources.
- Lack of Expertise: Analyzing RMM data requires specialized skills and expertise.
- Integration Issues: Integrating RMM tools with other security tools can be challenging.
Best Practices
- Prioritize Critical Assets: Focus on monitoring and protecting the most critical assets in your IT environment.
- Establish Baselines: Establish baselines of normal system and user behavior to more easily identify anomalies.
- Automate Threat Detection: Use automation to detect and respond to threats as quickly as possible.
- Continuously Improve: Continuously monitor and improve your RMM analytics program.
- Train Your Staff: Invest in training your staff on how to use RMM tools for cybersecurity.
- Document Everything: Maintain detailed documentation of your RMM configuration, policies, and procedures.
Conclusion
Cybersecurity threat detection through RMM analytics is a powerful approach to enhancing security posture and mitigating risks. By leveraging the data collected by RMM tools, IT professionals can proactively identify and respond to threats before they cause significant damage. While implementing RMM analytics can be challenging, the benefits are well worth the effort. By following the best practices outlined in this article, organizations can effectively leverage RMM analytics to improve their cybersecurity defenses and protect their critical assets.
As the threat landscape continues to evolve, RMM analytics will become increasingly important for organizations of all sizes. By investing in RMM tools and developing the necessary expertise, businesses can stay ahead of the curve and protect themselves from the ever-growing threat of cyberattacks.
Ultimately, a layered security approach that incorporates RMM analytics, alongside other security measures, is essential for creating a robust and resilient cybersecurity defense. Embrace the power of RMM, and you’ll be well on your way to a more secure and protected IT environment.
Conclusion
In conclusion, leveraging Remote Monitoring and Management (RMM) analytics for cybersecurity threat detection represents a significant advancement in proactive security posture. Throughout this article, we’ve explored how the vast amounts of data generated by RMM tools, when properly analyzed, can provide invaluable insights into potential vulnerabilities and malicious activities that might otherwise go unnoticed. By transforming raw data into actionable intelligence, organizations can significantly reduce their attack surface and minimize the impact of potential breaches. The ability to identify anomalies, track user behavior, and correlate events across diverse endpoints offers a powerful defense mechanism against increasingly sophisticated cyber threats.
Ultimately, the integration of RMM analytics into a comprehensive security strategy is no longer a luxury, but a necessity. As cyber threats continue to evolve, organizations must embrace proactive measures to safeguard their sensitive data and critical infrastructure. We encourage you to consider how your organization can better utilize RMM data to enhance its threat detection capabilities. Explore available RMM security features, investigate third-party analytics solutions, and most importantly, prioritize the development of a robust security strategy that incorporates these powerful tools. To learn more about advanced cybersecurity solutions and how they can benefit your organization, please visit our cybersecurity resource page.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ) about Cybersecurity Threat Detection through RMM Analytics
How can using RMM analytics help in proactively identifying and preventing cybersecurity threats before they impact my business?
RMM (Remote Monitoring and Management) analytics play a crucial role in proactive cybersecurity threat detection. By continuously monitoring various endpoints and network activities, RMM tools gather vast amounts of data. Analyzing this data allows for the identification of unusual patterns, anomalies, and deviations from established baselines. For example, a sudden surge in network traffic from a specific device or an unusual number of failed login attempts can signal a potential security breach. RMM analytics can also detect the presence of unauthorized software installations or processes running in the background, indicating malware infection. By identifying these early warning signs, businesses can take immediate action to mitigate the threat, such as isolating the affected device or implementing security patches, preventing significant damage and data loss. This proactive approach is significantly more effective than reactive measures taken after a breach has already occurred.
What specific types of security threats can be detected using RMM analytics, and how effective is it against advanced persistent threats (APTs)?
RMM analytics are effective at detecting a wide range of cybersecurity threats, including malware infections, phishing attempts, ransomware attacks, insider threats, and unauthorized access attempts. By analyzing system logs, network traffic, and user behavior, RMM tools can identify indicators of compromise (IOCs) associated with these threats. When it comes to Advanced Persistent Threats (APTs), RMM analytics can be a valuable layer of defense. APTs are characterized by their stealth and long-term presence within a network. While no single tool can guarantee complete protection against APTs, RMM analytics can help detect subtle anomalies and suspicious activities that might otherwise go unnoticed. For instance, an APT might involve lateral movement within the network or exfiltration of data over an extended period. The continuous monitoring and analysis capabilities of RMM tools can help uncover these patterns, allowing security teams to investigate and neutralize the threat before significant damage occurs. The effectiveness is increased when integrated with other security measures like endpoint detection and response (EDR) systems.
How do I choose the right RMM solution with strong analytics capabilities for cybersecurity threat detection, and what key features should I look for?
Choosing the right RMM solution with robust analytics is crucial for effective cybersecurity threat detection. Start by evaluating your specific needs and the size of your IT infrastructure. Look for RMM solutions that offer comprehensive monitoring capabilities, including real-time data collection from endpoints, servers, and network devices. Key features to consider include: Advanced Threat Intelligence (integration with threat feeds to identify known malicious actors and patterns), Behavioral Analysis (detecting anomalous user and system behavior that deviates from established baselines), Log Management and Analysis (centralized collection and analysis of logs from various sources), Automated Alerting and Reporting (configurable alerts based on predefined thresholds and customizable reports for security analysis), and Integration with other security tools (compatibility with SIEM, EDR, and other security solutions for enhanced threat detection and response). Also, consider the vendor’s reputation, customer reviews, and the availability of support and training. A user-friendly interface and clear documentation are essential for efficient operation and maximizing the value of the RMM solution.