In today’s complex IT landscape, keeping systems patched and secure is a constant battle. Think of it like this: your network is a castle, and software vulnerabilities are cracks in the walls. Hackers are always looking for those cracks to exploit. Manually patching every system, across every location, is not only incredibly time-consuming but also prone to human error. It’s like trying to patch every brick in that castle, one by one, with a trowel and a prayer. Sounds exhausting, right?
That’s where Remote Monitoring and Management (RMM) platforms come to the rescue, offering a powerful way to automate patch management. RMM isn’t just about monitoring; it’s about proactive management, and patch management is a key component of that. It’s like having a dedicated team of skilled masons constantly inspecting and repairing the castle walls, automatically, and with precision. By automating the process, you can significantly reduce your attack surface, improve security posture, and free up valuable IT resources to focus on more strategic initiatives.

This article will delve into the world of automating patch management through RMM, exploring its features, benefits, and practical considerations. We’ll cover everything from understanding the basics of patch management to implementing an effective RMM-driven strategy. Consider this your complete guide to turning a reactive, manual patching process into a proactive, automated security powerhouse. So, let’s get started and explore how to fortify your IT infrastructure against modern threats.
Understanding the Basics of Patch Management
Patch management is the process of acquiring, testing, and installing code changes (patches) on existing software applications and operating systems. These patches address vulnerabilities, fix bugs, and improve performance. In essence, it’s like providing regular maintenance to your software to keep it running smoothly and securely.
Why is Patch Management Important?
The importance of patch management cannot be overstated. Here’s why it’s crucial:
- Security: Patches often address security vulnerabilities that hackers can exploit to gain unauthorized access to your systems and data.
- Compliance: Many regulatory frameworks (e.g., HIPAA, PCI DSS, GDPR) require organizations to maintain up-to-date software and systems as part of their compliance obligations.
- Stability: Patches can fix bugs and improve the stability and performance of your software, reducing downtime and improving user experience.
- Feature Enhancements: Some patches include new features or improvements to existing functionality.
The Challenges of Manual Patch Management
Manually managing patches across a large number of devices is a daunting task. Some of the key challenges include:
- Time-Consuming: Manually checking for, downloading, and installing patches on each device is extremely time-consuming.
- Error-Prone: Manual processes are prone to human error, such as missing patches or installing them incorrectly.
- Lack of Visibility: It can be difficult to track which devices have been patched and which haven’t, leading to gaps in your security posture.
- Inconsistent Application: Ensuring patches are applied consistently across all devices can be challenging, especially in distributed environments.
- Testing Difficulties: Thoroughly testing patches before deploying them to production systems can be a complex and time-consuming process.
What is RMM and How Does It Help?
Remote Monitoring and Management (RMM) is a software platform used by IT professionals to remotely monitor, manage, and support client systems and networks. Think of it as your central command center for all things IT management. RMM tools provide a comprehensive suite of features that enable IT teams to proactively identify and resolve issues before they impact users or the business.
Key Features of RMM Platforms
While specific features vary depending on the vendor, most RMM platforms offer the following core capabilities:. Managing IT infrastructure effectively often involves a comprehensive approach, and RMM is a key part of that strategy
.
- Remote Access: Enables IT professionals to remotely access and control client devices for troubleshooting and support.
- Monitoring: Provides real-time monitoring of system performance, network health, and security events.
- Automation: Automates routine tasks such as patch management, software deployment, and script execution.
- Alerting: Generates alerts when critical issues are detected, allowing IT teams to respond quickly.
- Reporting: Provides detailed reports on system health, security posture, and performance trends.
- Asset Management: Tracks hardware and software assets, providing a centralized inventory of IT resources.
How RMM Facilitates Patch Management
RMM platforms streamline and automate the patch management process by:
- Automated Patch Scanning: Regularly scans all managed devices for missing patches.
- Centralized Patch Deployment: Allows IT professionals to deploy patches to multiple devices simultaneously from a central console.
- Scheduling and Automation: Enables scheduling of patch deployments to occur automatically during off-peak hours.
- Patch Testing and Approval: Provides features for testing patches in a controlled environment before deploying them to production systems.
- Reporting and Compliance: Generates reports on patch status and compliance, providing evidence of due diligence for regulatory requirements.
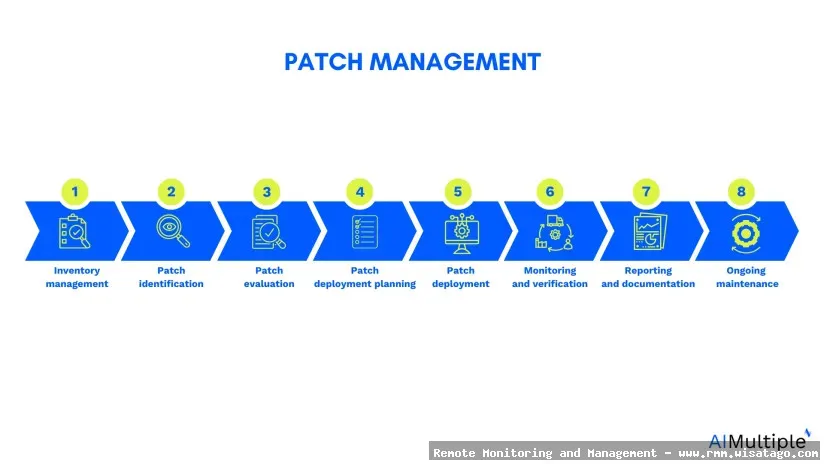
Automating Patch Management with RMM: A Step-by-Step Guide
Implementing automated patch management through RMM involves a series of steps. Here’s a general guide to get you started:
Step 1: Choose the Right RMM Platform
Selecting the right RMM platform is crucial. Consider factors such as:
- Features: Does the platform offer the features you need, including robust patch management capabilities?
- Scalability: Can the platform scale to meet your growing needs?
- Integration: Does the platform integrate with your existing IT tools and systems?
- Pricing: Is the pricing model affordable and predictable?
- Support: Does the vendor offer reliable technical support?
Step 2: Configure Patch Management Settings
Once you’ve selected an RMM platform, configure the patch management settings to align with your organization’s policies. This includes:
- Patch Approval Process: Define the process for approving patches before deployment. Some RMMs allow for automatic approval of certain patch types (e.g., critical security updates).
- Patch Deployment Schedules: Schedule patch deployments to occur during off-peak hours to minimize disruption to users.
- Reboot Policies: Configure reboot policies to ensure that devices are rebooted after patch installation when necessary.
- Exclusion Lists: Create exclusion lists to prevent certain patches from being installed on specific devices or groups of devices.
Step 3: Test Patches in a Staging Environment
Before deploying patches to production systems, it’s essential to test them in a staging environment. This helps identify any potential compatibility issues or unexpected behavior.
- Create a Test Group: Create a test group of devices that closely resemble your production environment.
- Deploy Patches to the Test Group: Deploy the patches to the test group and monitor for any issues.
- Document Findings: Document any issues encountered during testing and work with the vendor to resolve them before deploying the patches to production.
Step 4: Deploy Patches to Production Systems
Once you’ve tested the patches and are confident that they are safe to deploy, you can deploy them to your production systems. Use the RMM platform to schedule the deployments and monitor the progress.

- Phased Rollout: Consider a phased rollout, deploying patches to a small group of users first and then gradually expanding the deployment to the entire organization.
- Monitor Deployment Progress: Use the RMM platform to monitor the deployment progress and identify any devices that are experiencing issues.
- Communicate with Users: Communicate with users about the patch deployments and any potential downtime.
Step 5: Monitor and Report on Patch Status
After the patches have been deployed, monitor the patch status and generate reports to ensure that all devices are up-to-date. Use the RMM platform to identify any devices that are still missing patches and take corrective action.
- Regular Reporting: Generate regular reports on patch status and compliance.
- Identify Non-Compliant Devices: Identify any devices that are not compliant with your patch management policies.
- Remediate Non-Compliant Devices: Take corrective action to remediate non-compliant devices, such as manually installing the missing patches or troubleshooting deployment issues.
Benefits of Automating Patch Management Through RMM
Automating patch management with RMM offers numerous benefits, including:
- Improved Security: Reduces the attack surface by ensuring that all systems are patched with the latest security updates.
- Reduced Risk: Minimizes the risk of security breaches and data loss.
- Increased Efficiency: Frees up IT resources to focus on more strategic initiatives.
- Enhanced Compliance: Helps organizations meet regulatory compliance requirements.
- Improved System Stability: Reduces downtime and improves system performance.
- Centralized Management: Provides a centralized view of patch status across all managed devices.
Challenges and Considerations
While automating patch management with RMM offers significant benefits, there are also some challenges and considerations to keep in mind:
- Initial Setup and Configuration: Setting up and configuring the RMM platform can be time-consuming and require technical expertise.
- Patch Testing: Thoroughly testing patches before deploying them to production systems is crucial to avoid compatibility issues.
- Vendor Compatibility: Ensure that the RMM platform supports the operating systems and applications used in your environment.
- Network Bandwidth: Patch deployments can consume significant network bandwidth, especially in large environments.
- User Disruption: Patch deployments can sometimes disrupt users, especially if reboots are required.
- Ongoing Maintenance: The RMM platform requires ongoing maintenance and updates to ensure that it is functioning correctly.
Conclusion
Automating patch management through RMM is a critical component of a robust security strategy. By automating the process, organizations can significantly reduce their attack surface, improve security posture, and free up valuable IT resources. While there are some challenges and considerations to keep in mind, the benefits of automating patch management far outweigh the risks. By following the steps outlined in this guide, you can implement an effective RMM-driven patch management strategy and fortify your IT infrastructure against modern threats. Remember to choose the right RMM platform, configure the settings carefully, test patches thoroughly, and monitor the deployment progress. With a proactive and automated approach to patch management, you can rest assured that your systems are protected and secure.
Conclusion
In conclusion, automating patch management through your RMM platform is no longer a luxury, but a necessity in today’s evolving threat landscape. As we’ve explored, the benefits extend far beyond simply keeping systems up-to-date. It significantly reduces the attack surface, minimizes downtime, improves operational efficiency, and ultimately strengthens your overall security posture. The ability to proactively identify, test, and deploy patches across your entire IT infrastructure, all from a centralized console, empowers IT professionals to focus on strategic initiatives rather than being constantly reactive to emerging vulnerabilities.
The journey to automated patch management might seem daunting initially, but the long-term rewards are substantial. By carefully evaluating your current processes, selecting an RMM solution that aligns with your specific needs, and implementing a well-defined patch management policy, you can transform your approach to security and significantly reduce your risk. Don’t wait for the next major breach to highlight the importance of proactive patch management. Take control of your security today. Explore the capabilities of modern RMM platforms and discover how automation can revolutionize your IT operations. Consider a trial of an RMM solution or consult with a managed services provider to assess your needs and develop a tailored implementation plan. A good starting point is researching reputable RMM vendors and reading their case studies to see how other organizations have benefited from automated patch management. You can find valuable resources and vendor comparisons online to inform your decision.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ) about Automating Patch Management through RMM
How can I use an RMM (Remote Monitoring and Management) tool to automate patch management for Windows servers and workstations?
RMM tools significantly streamline patch management by automating key processes. You can typically configure your RMM to automatically scan managed devices (servers and workstations) for missing patches, identify vulnerabilities, and deploy updates according to a predefined schedule. This includes setting policies for different groups of devices, allowing you to prioritize critical servers. Most RMM platforms allow for testing patches on a subset of machines before widespread deployment, mitigating potential issues. Furthermore, RMMs provide centralized reporting on patch status, showing which devices are up-to-date and which require attention. This automation reduces manual effort, improves security posture, and ensures consistent patching across your entire infrastructure. Regularly reviewing and adjusting your patch management policies within the RMM is crucial for optimal effectiveness.
What are the benefits of automating my software patch management process using an RMM solution, and how does it improve cybersecurity?
Automating software patch management with an RMM solution offers numerous cybersecurity benefits. Firstly, it drastically reduces the time window between patch release and deployment, minimizing exposure to known vulnerabilities. This is critical because attackers often target systems with unpatched vulnerabilities within days or even hours of a patch being released. Secondly, automation ensures consistent patching across all managed devices, eliminating the risk of human error or oversight. Thirdly, RMMs provide detailed reporting and auditing capabilities, allowing you to track patch deployment status and identify any gaps in your security posture. By automating this process, you free up IT staff to focus on other critical security tasks, such as threat hunting and incident response, ultimately leading to a more robust and proactive cybersecurity defense. According to industry reports, a significant percentage of breaches exploit known vulnerabilities for which patches are available, highlighting the importance of timely patching.
What are the key features I should look for in an RMM tool to effectively automate third-party application patch management, beyond just operating system updates?
When selecting an RMM tool for automated third-party application patch management, consider these key features. Comprehensive Application Support is crucial; the RMM should support a wide range of commonly used applications like Adobe products, Java, web browsers (Chrome, Firefox), and other business-critical software. Look for a feature that allows you to add your own custom application definitions if needed. Automated Patch Detection and Deployment should scan for missing patches and deploy them automatically according to predefined policies. Customizable Patch Policies are essential for tailoring patch deployment to different groups of devices or applications. Testing and Staging Environments are important to test patches before widespread deployment to avoid potential compatibility issues. Finally, Reporting and Alerting provide visibility into patch status and alert you to any failures or vulnerabilities. Effective third-party patch management significantly reduces your attack surface and improves overall security.