In today’s dynamic IT landscape, containerization has revolutionized application deployment and management. Technologies like Docker and Kubernetes have become commonplace, offering scalability, portability, and efficiency. However, this shift also introduces new challenges, particularly in monitoring. Traditional monitoring tools often fall short when it comes to providing the granular visibility required to effectively manage containerized environments. This is where Remote Monitoring and Management (RMM) solutions step in, offering a powerful means to oversee and maintain these complex systems.
Think of it this way: you’ve built a fantastic new application, neatly packaged into containers and deployed across a cluster. It’s running smoothly, handling traffic like a champ. But what happens when something goes wrong? How do you pinpoint the issue when your application is spread across multiple containers, potentially running on different servers? Traditional monitoring might tell you a server is overloaded, but it won’t necessarily tell you which container is causing the problem, or why. This lack of detailed insight can lead to prolonged downtime and frustrated users.

This article will delve into the world of containerized application monitoring via RMM, exploring its benefits, features, and practical considerations. We’ll discuss how RMM solutions can provide the necessary visibility and control to ensure the health and performance of your containerized applications, helping you navigate the complexities of modern IT infrastructure. Consider this your complete guide to understanding how RMM can empower you to manage your containerized world effectively.
Understanding the Need for Containerized Application Monitoring
Containerized applications, while offering numerous advantages, present unique monitoring challenges. The ephemeral nature of containers, their dynamic scaling, and the sheer volume of instances can overwhelm traditional monitoring tools. We need tools that can keep up with the pace and complexity of these environments.
The Ephemeral Nature of Containers
Unlike traditional virtual machines, containers are often short-lived. They can be created and destroyed rapidly in response to changing demand. This means that a container that was perfectly healthy a few minutes ago might be gone, making it difficult to track down the root cause of issues. RMM solutions designed for container monitoring can dynamically discover and monitor containers as they come and go, providing real-time insights into their performance.
Dynamic Scaling and Orchestration
Container orchestration platforms like Kubernetes automatically scale applications based on predefined metrics. This dynamic scaling can lead to a constantly shifting landscape of containers. An RMM solution needs to be able to adapt to these changes, automatically adjusting its monitoring configuration as containers are added, removed, or moved between hosts.
Increased Complexity
Containerized applications are often composed of multiple microservices, each running in its own container. This distributed architecture can make it difficult to understand the interactions between different components and identify bottlenecks. RMM solutions can provide end-to-end visibility into the entire application stack, allowing you to trace requests and identify performance issues across multiple containers.
Benefits of Using RMM for Containerized Application Monitoring
Implementing an RMM solution for containerized application monitoring offers a wide range of benefits, from improved performance and reduced downtime to enhanced security and compliance.
Improved Performance and Availability
By providing real-time visibility into container performance, RMM solutions allow you to proactively identify and address issues before they impact users. This can lead to improved application performance and reduced downtime. For example, if an RMM solution detects that a container is consuming excessive CPU resources, you can take action to reallocate resources or optimize the container’s configuration.
Faster Troubleshooting and Resolution
When issues do occur, RMM solutions can help you quickly pinpoint the root cause and resolve them. By providing detailed metrics and logs, you can identify the affected containers, understand the nature of the problem, and take corrective action. This can significantly reduce the time it takes to resolve incidents and minimize the impact on users.

Enhanced Security
RMM solutions can also help you improve the security of your containerized applications. By monitoring container images for vulnerabilities and detecting suspicious activity, you can prevent security breaches and protect sensitive data. For example, an RMM solution might alert you if a container is attempting to access unauthorized resources or if it’s running a vulnerable version of a software library.
Simplified Compliance
Many industries are subject to strict regulatory requirements regarding data security and compliance. RMM solutions can help you meet these requirements by providing detailed audit trails of container activity. This can make it easier to demonstrate compliance to auditors and avoid costly penalties.
Key Features of RMM Solutions for Container Monitoring
Not all RMM solutions are created equal when it comes to container monitoring. Look for solutions that offer the following key features:
Automatic Discovery and Inventory
The RMM solution should automatically discover and inventory all containers in your environment, providing a real-time view of your container landscape. This includes identifying the container image, the host it’s running on, and its current status.
Real-Time Performance Monitoring
The solution should provide real-time monitoring of key container metrics, such as CPU usage, memory consumption, network traffic, and disk I/O. This allows you to identify performance bottlenecks and proactively address issues.
Log Aggregation and Analysis
The solution should aggregate logs from all containers in your environment, making it easy to search and analyze them. This is essential for troubleshooting issues and identifying security threats.
Alerting and Notification
The solution should provide customizable alerting and notification capabilities, allowing you to be notified when critical events occur. This ensures that you can respond quickly to issues and minimize their impact.
Integration with Container Orchestration Platforms
The solution should integrate seamlessly with container orchestration platforms like Kubernetes, allowing you to monitor the health and performance of your entire cluster. This includes monitoring the status of nodes, pods, and services.
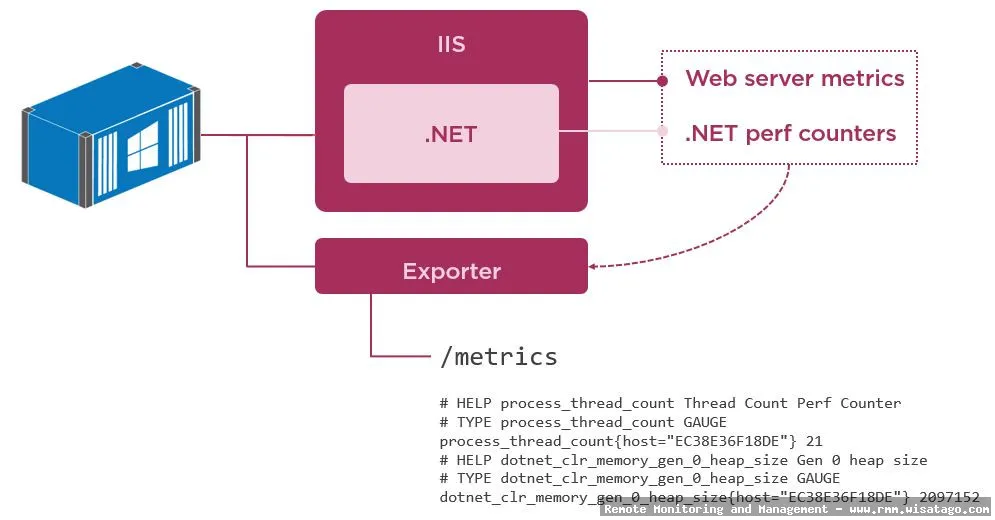
Security Monitoring and Vulnerability Scanning
The solution should provide security monitoring and vulnerability scanning capabilities, helping you identify and address security risks in your container environment. This includes scanning container images for vulnerabilities and detecting suspicious activity.
Practical Considerations for Implementing RMM in Containerized Environments
Implementing an RMM solution for containerized application monitoring requires careful planning and execution. Here are some practical considerations to keep in mind:
Choosing the Right RMM Solution
Selecting the right RMM solution is crucial for success. Consider your specific needs and requirements, and evaluate different solutions based on their features, capabilities, and pricing. Look for solutions that are specifically designed for container monitoring and that integrate well with your existing infrastructure.
Configuring the RMM Solution
Once you’ve selected an RMM solution, you need to configure it to monitor your containerized applications. This includes defining the metrics you want to track, setting up alerts and notifications, and configuring log aggregation and analysis.
Integrating with Existing Tools
Your RMM solution should integrate seamlessly with your existing tools, such as your monitoring dashboards, ticketing systems, and security information and event management (SIEM) systems. This will allow you to streamline your workflows and improve collaboration.
Training Your Team
It’s important to train your team on how to use the RMM solution effectively. This includes teaching them how to monitor container performance, troubleshoot issues, and respond to alerts.
Continuous Monitoring and Optimization
Monitoring your containerized applications is an ongoing process. You need to continuously monitor performance, identify areas for improvement, and optimize your configuration. This will ensure that your applications are running smoothly and efficiently.
Challenges of Containerized Application Monitoring with RMM
While RMM offers significant advantages, implementing it within containerized environments isn’t without its challenges. Understanding these potential hurdles is crucial for successful adoption.

Data Overload and Noise
The sheer volume of data generated by containerized applications can be overwhelming. RMM solutions need to effectively filter out noise and prioritize critical information to avoid alert fatigue. Proper configuration and intelligent alerting are essential.
Dynamic Infrastructure Changes
The constant churn of containers, scaling events, and updates can make it difficult to maintain a consistent view of the environment. RMM solutions must be highly adaptable and capable of automatically adjusting to these changes.
Security Concerns in Microservices
The distributed nature of microservices architectures introduces new security challenges. RMM solutions need to provide comprehensive security monitoring across all containers and services, including vulnerability scanning and threat detection.
Cost Considerations
The cost of RMM solutions can vary depending on the number of containers being monitored and the features required. It’s important to carefully evaluate pricing models and ensure that the solution provides a good return on investment.
The Future of Containerized Application Monitoring with RMM
The future of containerized application monitoring with RMM is bright, with continued advancements in technology and increasing adoption of containerization. We can expect to see:
Increased Automation
RMM solutions will become increasingly automated, using machine learning and artificial intelligence to proactively identify and resolve issues. This will reduce the need for manual intervention and improve efficiency.
Enhanced Security Capabilities
RMM solutions will offer more advanced security capabilities, such as runtime application self-protection (RASP) and behavioral analysis, to protect containerized applications from emerging threats.
Deeper Integration with DevOps Tools
RMM solutions will integrate more deeply with DevOps tools, such as CI/CD pipelines and infrastructure-as-code platforms, to streamline the development and deployment process.

Improved Observability
RMM solutions will provide even greater observability into containerized applications, allowing you to understand the performance and behavior of your applications in unprecedented detail.
In conclusion, containerized application monitoring via RMM is essential for ensuring the health, performance, and security of modern applications. By understanding the benefits, features, and challenges of RMM, you can effectively manage your containerized environment and unlock the full potential of this powerful technology. Don’t wait until a critical issue arises; invest in a robust RMM solution today and gain the peace of mind that comes with knowing your applications are being monitored and protected.
Conclusion
In summary, containerized application monitoring via RMM offers a powerful and streamlined approach to managing the complexities of modern, cloud-native environments. By leveraging the capabilities of RMM platforms, organizations can gain unprecedented visibility into the performance and health of their containerized applications, enabling proactive problem resolution, optimized resource allocation, and improved overall service reliability. The integration of RMM with container orchestration platforms like Kubernetes allows for centralized monitoring, automated alerting, and efficient management of distributed applications, ultimately leading to significant cost savings and increased operational efficiency.
The shift towards containerization is undeniable, and adopting a robust monitoring strategy is no longer optional but crucial for success. Investing in an RMM solution that effectively monitors your containerized applications will empower your teams to proactively address issues, optimize performance, and ensure a seamless user experience. If you’re ready to take your container monitoring to the next level, we encourage you to explore the various RMM solutions available and discover how they can transform your application management strategy. Learn more about leading container monitoring solutions here.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ) about Containerized Application Monitoring via RMM
How can I leverage my existing Remote Monitoring and Management (RMM) tool to monitor the health and performance of containerized applications?
Leveraging your existing RMM tool for monitoring containerized applications often involves integrating it with container orchestration platforms like Kubernetes or Docker Swarm. Many RMM solutions offer agents or plugins that can be deployed within containers to collect performance metrics such as CPU usage, memory consumption, network I/O, and disk I/O. These metrics are then reported back to the RMM dashboard for centralized monitoring and alerting. Furthermore, you can configure health checks within your container orchestration platform and integrate those status updates into your RMM system to receive notifications when containers become unhealthy or fail. Effective container monitoring with RMM requires understanding your RMM’s capabilities and the specific needs of your containerized environment. Look for RMM solutions that support container-specific metrics and alerting.
What are the key performance indicators (KPIs) I should be tracking when monitoring containerized applications through my RMM platform?
When monitoring containerized applications via RMM, several key performance indicators (KPIs) are crucial for ensuring optimal performance and identifying potential issues. Essential KPIs include CPU utilization (to identify resource bottlenecks), memory usage (to prevent out-of-memory errors), network latency (to assess communication delays between containers), disk I/O (to monitor storage performance), and container restart counts (to detect instability). Additionally, you should track application-specific metrics, such as request response times, error rates, and transaction volumes. Monitoring these KPIs through your RMM platform allows you to proactively identify performance bottlenecks, troubleshoot issues, and ensure the overall health and stability of your containerized applications. Setting appropriate thresholds and alerts within your RMM is vital for timely intervention. For more information, you can refer to RMM as an additional resource.
What are the security considerations when using an RMM tool to monitor containerized applications in a production environment, and how can I mitigate potential risks?
Security is paramount when using an RMM tool to monitor containerized applications. A primary concern is the potential attack surface introduced by the RMM agent running within the containers. Mitigation strategies include ensuring the RMM agent is regularly updated with the latest security patches and using strong authentication mechanisms for access control. Implement network segmentation to restrict communication between containers and the RMM server, minimizing the impact of a potential breach. Regularly audit the RMM configuration and access logs to detect any suspicious activity. Consider using a dedicated RMM instance for monitoring containerized environments to isolate it from other systems. Finally, implement robust vulnerability scanning and penetration testing to identify and address potential security weaknesses in both the containers and the RMM infrastructure. Always follow the principle of least privilege for RMM agent permissions.