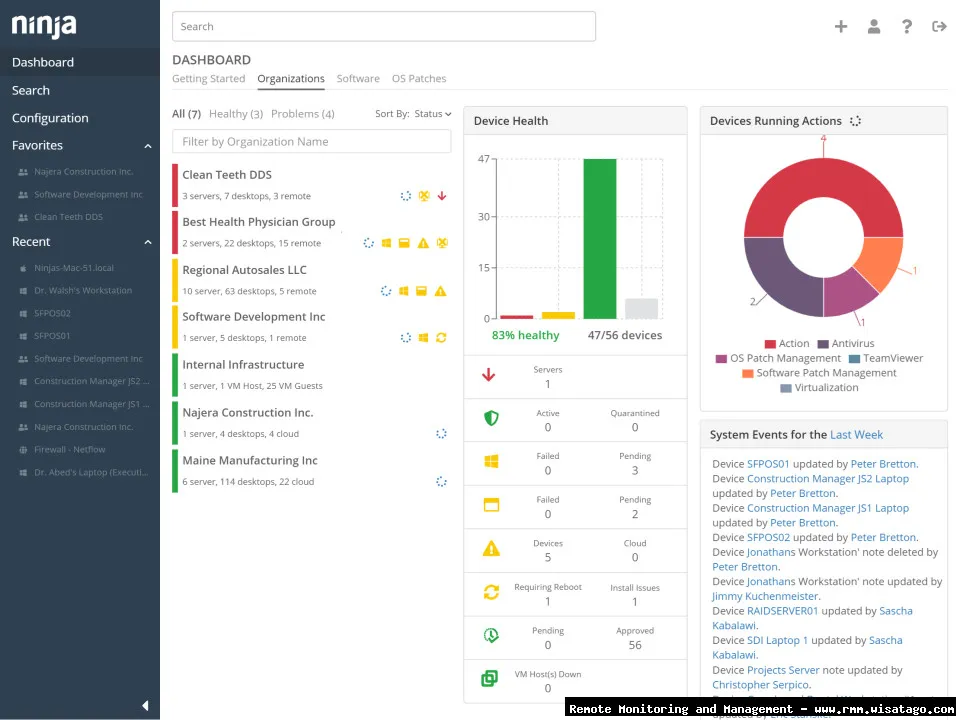
In the ever-evolving landscape of IT management, staying ahead of potential issues is paramount. Reactive firefighting is no longer a sustainable strategy. Businesses need proactive solutions that anticipate problems before they impact productivity and profitability. This is where Enterprise Remote Monitoring and Management (RMM) platforms shine, offering a centralized hub for overseeing the health and performance of your entire IT infrastructure. But the true power of RMM lies in its customization capabilities, particularly the ability to create and deploy custom monitoring templates.
Custom monitoring templates are essentially pre-configured sets of monitoring parameters, thresholds, and alerts tailored to specific devices, applications, or business needs. Think of them as blueprints for proactive IT management, allowing you to define exactly what you want to monitor, how often, and what actions to take when certain conditions are met. By leveraging these templates, you can move beyond generic monitoring and focus on the metrics that truly matter to your organization, ensuring optimal performance and minimizing downtime.

This guide will delve into the world of custom monitoring templates in Enterprise RMM, exploring their benefits, features, and practical applications. We’ll discuss how to create effective templates, best practices for implementation, and the challenges you might encounter along the way. Whether you’re a seasoned IT professional or just starting your RMM journey, this article will provide you with the knowledge and insights you need to harness the power of custom monitoring and transform your IT management strategy.
What are Custom Monitoring Templates?
At its core, a custom monitoring template is a pre-defined configuration within your RMM system that dictates how specific aspects of your IT environment are monitored. Instead of manually configuring monitoring settings for each device or application individually, you create a template once and then apply it to multiple endpoints simultaneously. This saves significant time and ensures consistency across your entire infrastructure.
Key Components of a Custom Monitoring Template
A typical custom monitoring template will include the following components:. Effective IT management often requires a proactive approach, which is where RMM becomes a valuable asset
.
- Monitored Parameters: These are the specific metrics or indicators that the RMM system will track. Examples include CPU utilization, memory usage, disk space, network latency, application uptime, and service status.
- Thresholds: Thresholds define the acceptable range of values for each monitored parameter. When a parameter exceeds or falls below a defined threshold, an alert is triggered. For instance, you might set a threshold to trigger an alert when CPU utilization reaches 80%.
- Alerting Mechanisms: This determines how you are notified when a threshold is breached. Common options include email notifications, SMS messages, and integration with ticketing systems.
- Remediation Actions: Some RMM systems allow you to define automated remediation actions that are triggered when an alert is generated. This could include restarting a service, killing a process, or running a script to automatically resolve the issue.
- Scheduling: You can schedule when the monitoring template is active. This is useful for monitoring tasks that only need to be performed during specific times, such as end-of-day backups.
Benefits of Using Custom Monitoring Templates
Implementing custom monitoring templates offers a wide range of benefits for IT teams, significantly improving efficiency and reducing downtime.
Increased Efficiency and Reduced Time
Manual configuration of monitoring settings for each device is a time-consuming and error-prone process. Custom templates allow you to configure monitoring once and deploy it across multiple devices, significantly reducing the time spent on repetitive tasks. This frees up your IT staff to focus on more strategic initiatives.
Improved Consistency and Standardization
By using templates, you ensure that monitoring is consistent across your entire IT environment. This eliminates discrepancies that can arise from manual configuration and makes it easier to identify and troubleshoot issues. Standardization also simplifies reporting and compliance efforts.
Proactive Problem Detection and Resolution
Custom templates allow you to monitor the specific metrics that are critical to your business. By setting appropriate thresholds and alerts, you can identify potential problems before they impact end-users. Automated remediation actions can even resolve some issues automatically, further minimizing downtime.

Enhanced Visibility and Control
Custom monitoring provides a comprehensive view of your IT infrastructure, giving you greater visibility into the health and performance of your systems. This allows you to make informed decisions about resource allocation, capacity planning, and security.
Reduced Downtime and Improved Business Continuity
By proactively detecting and resolving issues, custom monitoring helps to minimize downtime and improve business continuity. This can have a significant impact on productivity, revenue, and customer satisfaction.
Creating Effective Custom Monitoring Templates: A Step-by-Step Guide
Creating effective custom monitoring templates requires careful planning and a thorough understanding of your IT environment. Here’s a step-by-step guide to help you get started:
1. Identify Your Monitoring Needs
The first step is to identify the specific devices, applications, and services that you need to monitor. Consider the critical business processes that rely on these systems and the metrics that are most important for ensuring their optimal performance. For example, if you’re running an e-commerce website, you might want to monitor web server uptime, database performance, and transaction success rates.
2. Define Monitored Parameters and Thresholds
Once you’ve identified your monitoring needs, you need to define the specific parameters that you want to track and the thresholds that will trigger alerts. Choose parameters that are relevant to the health and performance of the systems you’re monitoring. Set thresholds that are appropriate for your environment and that will provide early warning of potential problems. Avoid setting thresholds too low, as this can lead to alert fatigue.
3. Configure Alerting Mechanisms
Configure the alerting mechanisms to ensure that you are notified promptly when a threshold is breached. Choose the notification method that is most appropriate for your team and the severity of the alert. For critical issues, you might want to send SMS messages to on-call personnel. For less urgent issues, email notifications may suffice.
4. Implement Automated Remediation Actions (Optional)
If your RMM system supports automated remediation actions, consider implementing them to automatically resolve common issues. This can save time and reduce the need for manual intervention. However, be sure to test remediation actions thoroughly before deploying them to production to avoid unintended consequences.
5. Test and Refine Your Templates
After you’ve created your templates, it’s important to test them thoroughly to ensure that they are working as expected. Simulate different scenarios to verify that alerts are triggered correctly and that remediation actions are effective. Based on your testing, refine your templates as needed to optimize their performance and accuracy.
6. Document Your Templates
Document your templates to provide a clear understanding of their purpose, configuration, and intended use. This will make it easier to maintain and troubleshoot your templates over time. Include information about the monitored parameters, thresholds, alerting mechanisms, and remediation actions.
Real-World Use Cases for Custom Monitoring Templates
Custom monitoring templates can be used in a wide variety of scenarios to improve IT management and reduce downtime. Here are a few real-world examples:
Monitoring Database Servers
Create a template to monitor key database server metrics such as CPU utilization, memory usage, disk space, query response time, and connection counts. Set thresholds to trigger alerts when these metrics exceed acceptable levels. Implement automated remediation actions to restart the database service if it becomes unresponsive.
Monitoring Web Servers
Create a template to monitor web server uptime, response time, error rates, and traffic volume. Set thresholds to trigger alerts when the web server becomes unavailable or when response times are slow. Implement automated remediation actions to restart the web server if it fails.
Monitoring Network Devices
Create a template to monitor network device availability, bandwidth utilization, and latency. Set thresholds to trigger alerts when network devices become unavailable or when bandwidth utilization is high. This can help you identify network bottlenecks and prevent performance issues.
Monitoring Virtual Machines
Create a template to monitor virtual machine CPU utilization, memory usage, disk space, and network performance. Set thresholds to trigger alerts when these metrics exceed acceptable levels. This can help you optimize virtual machine resource allocation and prevent performance issues.

Monitoring Specific Applications
Create a template to monitor the uptime, performance, and error rates of specific applications. This can help you identify and resolve application-related issues quickly and efficiently. For example, you could monitor the performance of a critical business application and trigger alerts when it becomes slow or unresponsive.
Challenges and Considerations
While custom monitoring templates offer significant benefits, there are also some challenges and considerations to keep in mind.
Alert Fatigue
Setting thresholds too low can lead to alert fatigue, where IT staff are overwhelmed with notifications. This can reduce their ability to respond effectively to critical issues. To avoid alert fatigue, carefully consider the appropriate thresholds for each monitored parameter and prioritize alerts based on their severity.
Template Maintenance
Custom monitoring templates need to be maintained and updated regularly to ensure that they remain accurate and effective. As your IT environment evolves, you may need to adjust thresholds, add new monitored parameters, or modify remediation actions. Establish a process for reviewing and updating your templates on a regular basis.
Complexity
Creating and managing a large number of custom monitoring templates can become complex. Use a consistent naming convention and documentation to help you keep track of your templates and their purpose. Consider using template inheritance to create a hierarchy of templates, where common settings are inherited from a parent template.
Integration with Other Systems
Ensure that your RMM system integrates seamlessly with other IT management tools, such as ticketing systems and security information and event management (SIEM) systems. This will allow you to streamline your IT operations and improve incident response times.
Best Practices for Implementing Custom Monitoring Templates
To maximize the benefits of custom monitoring templates, follow these best practices:
- Start Small: Begin by creating templates for your most critical systems and applications.
- Focus on Key Metrics: Monitor the metrics that are most important for ensuring the health and performance of your systems.
- Set Realistic Thresholds: Avoid setting thresholds too low, as this can lead to alert fatigue.
- Automate Remediation Actions: Implement automated remediation actions to automatically resolve common issues.
- Test Thoroughly: Test your templates thoroughly before deploying them to production.
- Document Everything: Document your templates to provide a clear understanding of their purpose and configuration.
- Review and Update Regularly: Review and update your templates on a regular basis to ensure that they remain accurate and effective.
Conclusion
Custom monitoring templates are a powerful tool for proactive IT management. By leveraging these templates, you can improve efficiency, reduce downtime, and gain greater visibility into your IT environment. While there are some challenges to consider, the benefits of custom monitoring far outweigh the drawbacks. By following the best practices outlined in this guide, you can harness the power of custom monitoring and transform your IT management strategy. Embrace the proactive approach and watch your IT infrastructure thrive.
Conclusion
In conclusion, custom monitoring templates represent a paradigm shift in how enterprises manage their IT infrastructure within an RMM environment. By moving beyond generic, one-size-fits-all solutions, organizations can achieve a level of granularity and precision that directly addresses their unique operational needs and security posture. The ability to tailor monitoring parameters, thresholds, and alerts ensures that IT teams are focused on what truly matters, reducing alert fatigue and accelerating response times to critical issues.
Ultimately, the implementation of custom monitoring templates is an investment in efficiency, stability, and proactive problem-solving. If you’re ready to elevate your RMM strategy and gain unparalleled visibility into your IT environment, we encourage you to explore the possibilities that custom monitoring templates offer. Contact your RMM vendor or a qualified managed services provider today to learn more about how you can implement this powerful capability and unlock the full potential of your IT infrastructure monitoring. Visit our website at https://www.example.com/custom-monitoring to download a free guide on building effective custom monitoring templates.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ) about Custom Monitoring Templates in Enterprise RMM
How can I create a custom monitoring template in my Enterprise RMM software to monitor specific application performance metrics?
Creating custom monitoring templates in your Enterprise RMM software allows you to focus on the specific application performance metrics that are most critical to your business. Typically, you’ll start by accessing the template management section within your RMM platform. From there, you can create a new template and define the monitors you want to include. This usually involves selecting the type of monitor (e.g., CPU usage, memory consumption, disk I/O, network latency), specifying the target application or service, and setting threshold values. Ensure you configure appropriate alert levels (warning, critical) for each metric. You can also specify the frequency of monitoring checks. After defining your monitors, save the template and apply it to the relevant devices or groups within your managed environment. Testing the template on a small group of devices before widespread deployment is highly recommended to ensure accuracy and avoid false positives.
What are the benefits of using custom monitoring templates versus the default monitoring settings in my Enterprise RMM solution, and when should I consider creating them?
Default monitoring settings in Enterprise RMM solutions offer a general overview of system health, but custom monitoring templates provide a more tailored and granular approach. The primary benefit of custom templates is the ability to focus on specific metrics relevant to your organization’s unique needs and applications. This reduces alert fatigue by filtering out irrelevant notifications and allows for quicker identification of critical issues. You should consider creating custom templates when: 1) You need to monitor specific applications or services not covered by default settings. 2) You require more granular control over threshold values and alert levels. 3) You want to monitor custom scripts or processes. 4) You need to track metrics related to specific business goals or compliance requirements. 5) The default monitoring generates excessive or irrelevant alerts.
How do I effectively deploy and manage custom monitoring templates across multiple clients or sites within my Enterprise RMM, and what are some best practices?
Deploying and managing custom monitoring templates across multiple clients or sites in an Enterprise RMM requires a structured approach. Start by organizing clients and sites into logical groups based on their IT needs and application usage. Most RMM platforms allow you to apply templates to these groups. Leverage the RMM’s policy management features to automate template deployment and ensure consistent monitoring across all managed devices. Implement version control for your templates to track changes and easily revert to previous configurations if needed. Regularly review and update your templates to reflect evolving business requirements and security threats. Use reporting features to monitor the effectiveness of your templates and identify areas for improvement. Finally, document your templates thoroughly, including the purpose, metrics monitored, and alert thresholds, to facilitate troubleshooting and knowledge sharing within your team.