Edge computing is no longer a futuristic concept; it’s a present-day reality for many businesses. By processing data closer to the source, edge computing reduces latency, improves performance, and offers enhanced security. But this distributed architecture also presents new challenges for IT management. How do you monitor, maintain, and secure hundreds, or even thousands, of edge devices scattered across different locations? That’s where Remote Monitoring and Management (RMM) solutions step in, providing a centralized platform to manage this complex landscape.
Think of it like this: you used to manage a well-defined network within your office walls. Now, your network extends to remote factories, retail stores, wind farms – anywhere data is being generated and processed at the edge. Manually managing each of these locations individually simply isn’t scalable or cost-effective. RMM solutions offer the visibility and control needed to efficiently manage these distributed edge environments, ensuring uptime, security, and optimal performance.
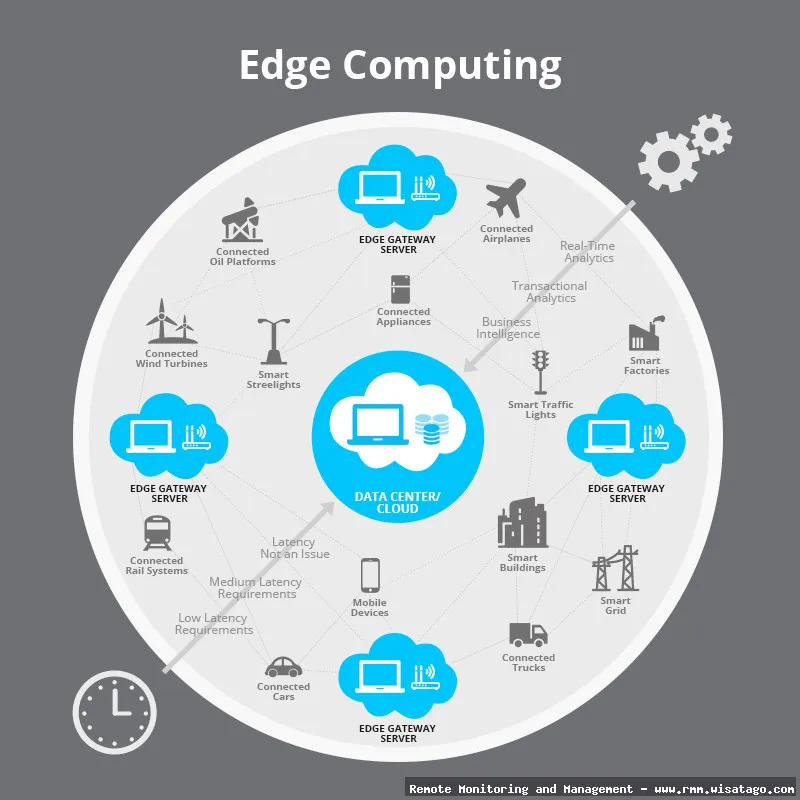
This article will delve into the world of edge computing management via RMM solutions. We’ll explore the key features, benefits, and considerations involved in leveraging RMM to effectively manage your edge infrastructure. We’ll cover real-world use cases, discuss the challenges you might face, and provide practical insights to help you make informed decisions about your edge management strategy. Consider this your complete guide to understanding how RMM can empower you to conquer the complexities of edge computing.
Understanding the Convergence of Edge Computing and RMM
Edge computing, at its core, is about bringing computation and data storage closer to the devices and sensors that are collecting data. This reduces the need to transmit vast amounts of data to a central cloud, leading to faster response times and reduced bandwidth consumption. RMM, traditionally used to manage on-premises and cloud infrastructure, is now evolving to address the unique needs of edge environments.
What is Edge Computing?
Edge computing involves processing data locally, on devices at the “edge” of the network, rather than relying solely on a centralized data center or cloud. This approach is crucial for applications that require low latency, such as autonomous vehicles, industrial automation, and real-time video analytics. Imagine a self-driving car that needs to make split-second decisions – it can’t afford to wait for data to travel to a distant server and back.
What is RMM?
Remote Monitoring and Management (RMM) is a suite of software tools used by IT professionals to remotely monitor, manage, and maintain client systems. This includes tasks like patching, software deployment, performance monitoring, and security management. RMM platforms provide a centralized dashboard where IT teams can gain visibility into the health and status of all managed devices, regardless of their location.
The Natural Synergy
The synergy between edge computing and RMM is clear. Edge deployments often involve a large number of geographically dispersed devices, making manual management impossible. RMM provides the necessary automation, remote access, and centralized control to effectively manage these distributed edge nodes. It allows IT teams to proactively identify and resolve issues, ensuring the smooth operation of edge applications and services.
Key Features of RMM Solutions for Edge Computing
Not all RMM solutions are created equal, especially when it comes to managing edge environments. Look for solutions that offer features specifically designed to address the unique challenges of edge computing.
Remote Monitoring and Alerting
This is the foundation of any good RMM solution. Real-time monitoring of edge devices allows you to identify potential problems before they impact performance. Customizable alerts can be configured to notify you of critical issues, such as high CPU usage, low disk space, or network connectivity problems. Specifically, consider RMMs that can monitor metrics relevant to edge devices such as specific sensor readings, data processing times, and latency between the edge and the cloud.
Remote Access and Control
Being able to remotely access and control edge devices is crucial for troubleshooting and resolving issues. RMM solutions should provide secure remote access capabilities, allowing IT technicians to connect to devices regardless of their location. This minimizes the need for on-site visits, saving time and money. Pay close attention to the security protocols used for remote access to ensure data is protected.

Patch Management
Keeping edge devices up-to-date with the latest security patches is essential for protecting against vulnerabilities. RMM solutions should automate the patch management process, ensuring that all devices are patched promptly and consistently. This includes operating system patches, application updates, and firmware updates. Consider solutions that support automated patch testing to avoid unexpected issues after deployment.
Software Deployment
Deploying software to a large number of edge devices can be a daunting task. RMM solutions streamline this process by allowing you to remotely deploy software packages to multiple devices simultaneously. This ensures that all devices are running the correct software versions and configurations. Look for features like silent installations and scheduled deployments to minimize disruption.
Automation and Scripting
Automation is key to efficiently managing a large number of edge devices. RMM solutions should provide robust automation and scripting capabilities, allowing you to automate routine tasks such as system maintenance, configuration changes, and security checks. This frees up IT staff to focus on more strategic initiatives. Consider using scripting to automate tasks like data backups, log file analysis, and performance optimization.
Security Management
Edge devices are often located in unsecured environments, making them vulnerable to attack. RMM solutions should provide security management features such as antivirus protection, intrusion detection, and endpoint security management. This helps to protect edge devices from malware, unauthorized access, and other security threats. Consider solutions that integrate with security information and event management (SIEM) systems for enhanced threat detection and response.
Reporting and Analytics
RMM solutions should provide comprehensive reporting and analytics capabilities, allowing you to track the performance of your edge infrastructure and identify areas for improvement. This includes reports on device uptime, resource utilization, security incidents, and patch compliance. Use these reports to optimize your edge deployments and improve overall efficiency.
Benefits of Using RMM for Edge Computing Management
Implementing an RMM solution for edge computing management offers numerous benefits, including:
Reduced Operational Costs
By automating routine tasks and minimizing the need for on-site visits, RMM can significantly reduce operational costs. Remote troubleshooting and automated patching save time and money, while proactive monitoring prevents costly downtime.
Improved Uptime and Reliability
RMM allows you to proactively identify and resolve issues before they impact performance, ensuring high uptime and reliability for your edge applications and services. Real-time monitoring and automated alerts enable you to respond quickly to potential problems.

Enhanced Security
RMM helps to protect edge devices from security threats by providing security management features such as antivirus protection, intrusion detection, and patch management. This minimizes the risk of data breaches and other security incidents.
Increased Efficiency
By automating routine tasks and providing centralized management, RMM frees up IT staff to focus on more strategic initiatives. This increases efficiency and allows you to get more value from your IT resources. Effective IT management is crucial for maintaining operational efficiency, and RMM provides a framework for achieving this through proactive monitoring and maintenance
.
Scalability
RMM solutions are designed to scale to manage a large number of devices, making them ideal for edge computing environments. You can easily add new devices to the RMM platform and manage them centrally, regardless of their location.
Challenges and Considerations
While RMM offers significant benefits for edge computing management, there are also some challenges and considerations to keep in mind.
Network Connectivity
Edge devices often operate in environments with limited or unreliable network connectivity. This can make it difficult to remotely monitor and manage these devices. Consider RMM solutions that can operate in offline or low-bandwidth environments, using features like store-and-forward data transmission.
Security
Edge devices are often located in unsecured environments, making them vulnerable to attack. It’s crucial to implement robust security measures to protect these devices from malware, unauthorized access, and other security threats. Ensure your RMM solution offers strong security features and that your IT staff is trained on security best practices.
Scalability
As your edge deployments grow, you’ll need an RMM solution that can scale to manage a large number of devices. Choose a solution that is designed for scalability and that can handle the increasing demands of your edge environment.
Integration
Integrating your RMM solution with other IT systems, such as your SIEM and ticketing systems, is crucial for streamlining your IT operations. Choose an RMM solution that offers robust integration capabilities and that can seamlessly integrate with your existing infrastructure.

Edge-Specific Monitoring
Traditional RMMs might not be fully equipped to monitor edge-specific metrics. Consider RMMs that have plugins or integrations specifically designed for the types of edge devices and applications you are using. This might include monitoring specific sensor data, data processing latency at the edge, or the health of edge-based AI models.
Real-World Use Cases
To illustrate the benefits of RMM in edge computing, let’s look at some real-world use cases.
Retail
Retail stores are increasingly using edge computing for tasks such as video analytics, inventory management, and point-of-sale (POS) systems. RMM can be used to remotely monitor and manage these edge devices, ensuring that they are running smoothly and securely. For example, an RMM solution can monitor the health of POS systems, automatically patch security vulnerabilities, and remotely troubleshoot issues with video analytics cameras.
Manufacturing
Manufacturers are using edge computing to improve efficiency and reduce downtime. RMM can be used to monitor industrial equipment, predict maintenance needs, and remotely troubleshoot issues. For example, an RMM solution can monitor the temperature and vibration of machinery, alert maintenance teams to potential problems, and remotely access equipment to diagnose and repair issues.
Healthcare
Healthcare providers are using edge computing for tasks such as remote patient monitoring, medical imaging, and telehealth. RMM can be used to securely manage these edge devices, ensuring patient data is protected and that critical applications are always available. For example, an RMM solution can monitor the performance of remote patient monitoring devices, automatically patch security vulnerabilities, and remotely troubleshoot issues with telehealth equipment.
Energy
Energy companies use edge computing to monitor remote assets like wind turbines and solar panels. RMM solutions can track performance, detect anomalies, and schedule preventative maintenance, minimizing downtime and maximizing energy production. For example, an RMM can monitor the output of a solar panel array, alert technicians to potential malfunctions, and remotely adjust settings to optimize energy generation.
Conclusion
Edge computing is transforming the way businesses operate, but it also presents new challenges for IT management. RMM solutions provide a powerful and effective way to manage these distributed edge environments, ensuring uptime, security, and optimal performance. By understanding the key features, benefits, and considerations involved in leveraging RMM for edge computing, you can make informed decisions about your edge management strategy and unlock the full potential of your edge deployments.
As edge computing continues to evolve, RMM solutions will play an increasingly important role in enabling businesses to effectively manage their distributed infrastructure. Investing in a robust RMM solution is a strategic move that can help you stay ahead of the curve and maximize the value of your edge investments.

Ultimately, the successful integration of RMM into your edge computing strategy requires a clear understanding of your specific business needs, a careful evaluation of available RMM solutions, and a commitment to ongoing monitoring and optimization. By taking a proactive approach, you can harness the power of RMM to conquer the complexities of edge computing and drive innovation across your organization.
Conclusion
As we’ve explored, effectively managing edge computing deployments is no longer a futuristic ideal but a present-day necessity for businesses seeking enhanced performance, reduced latency, and improved data security. The complexities inherent in distributed edge environments demand robust and streamlined management solutions. RMM platforms, with their proven capabilities in monitoring, automation, and remote support, offer a compelling answer. By leveraging RMM solutions, organizations can gain centralized visibility and control over their geographically dispersed edge infrastructure, ensuring consistent performance, simplified maintenance, and proactive issue resolution. This ultimately translates to a more agile, efficient, and resilient edge computing environment.
The integration of RMM into edge computing management represents a significant step toward unlocking the full potential of this transformative technology. The ability to remotely monitor device health, automate software updates, and proactively address security vulnerabilities across a distributed network is crucial for long-term success. If you’re considering deploying or already managing an edge computing infrastructure, we encourage you to investigate how an RMM solution can streamline your operations, improve your security posture, and ultimately drive greater business value. Explore the available RMM platforms and consider a trial to experience the benefits firsthand. Investing in the right management tools is an investment in the future of your edge.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ) about Edge Computing Management via RMM Solutions
How can I use Remote Monitoring and Management (RMM) software to effectively manage and monitor distributed edge computing devices?
RMM solutions offer a centralized platform to manage and monitor geographically dispersed edge computing devices. You can leverage RMM to perform several key tasks. Firstly, remote monitoring capabilities provide real-time insights into the health, performance, and security of edge devices, including CPU utilization, memory usage, and network connectivity. Secondly, remote management features allow for software patching, configuration updates, and troubleshooting without requiring on-site personnel. Thirdly, RMM platforms often include automation features to streamline routine tasks such as device onboarding, security policy enforcement, and alert management. By centralizing management and automating key processes, RMM significantly reduces the operational overhead associated with managing a distributed edge computing infrastructure, improving efficiency and minimizing downtime.
What are the key security benefits of using an RMM solution for managing edge computing environments, especially concerning endpoint security and data protection?
RMM solutions provide several crucial security benefits for edge computing environments. Firstly, they facilitate centralized security policy enforcement, ensuring consistent security configurations across all edge devices. This includes managing firewalls, antivirus software, and intrusion detection systems. Secondly, RMM enables proactive vulnerability management through automated patching and software updates, mitigating the risk of exploits. Thirdly, RMM solutions offer endpoint security capabilities, such as remote device wiping and lockdown, in case of theft or compromise. Furthermore, RMM platforms often include data protection features, such as data encryption and access control, to safeguard sensitive data stored and processed at the edge. By providing these security features, RMM helps organizations maintain a strong security posture and protect their edge computing infrastructure from cyber threats.
What specific features should I look for in an RMM platform to ensure it’s suitable for managing the unique challenges of an edge computing deployment, such as limited bandwidth and intermittent connectivity?
When selecting an RMM solution for edge computing, several features are critical. Firstly, look for bandwidth-efficient communication protocols. The RMM should minimize data transfer overhead to cope with limited bandwidth at the edge. Secondly, offline management capabilities are crucial. The RMM should be able to queue commands and updates to be executed when connectivity is restored, ensuring continuous operation even with intermittent connections. Thirdly, robust alerting and monitoring features are essential to quickly identify and address issues at the edge. The RMM should support customizable alerts based on various performance metrics. Furthermore, remote access and control features should be secure and optimized for low-bandwidth environments. Finally, ensure the RMM supports edge-specific operating systems and hardware commonly used in your deployment. Prioritizing these features will ensure your RMM can effectively manage the constraints and complexities of an edge computing environment.