In today’s dynamic business landscape, growth is the ultimate goal, but it also presents a unique set of challenges for IT departments. As enterprises expand, their IT infrastructure becomes increasingly complex, demanding more robust and scalable solutions. One critical component of a well-managed IT environment is Remote Monitoring and Management (RMM). RMM tools enable IT professionals to remotely monitor, manage, and support their clients’ or internal IT systems, ensuring optimal performance, security, and reliability. But what happens when a company experiences significant growth? The RMM solution that worked perfectly well for a smaller organization may quickly become inadequate, leading to inefficiencies, increased downtime, and ultimately, hindered growth. That’s where scalable RMM architecture comes into play.
Think of your IT infrastructure as a city’s road network. A small town can manage with a few simple roads, but as the town grows into a bustling metropolis, the infrastructure needs to scale. You need more roads, highways, and efficient traffic management systems to avoid gridlock. Similarly, a growing enterprise needs an RMM solution that can handle an increasing number of endpoints, servers, and network devices without sacrificing performance or functionality. A scalable RMM architecture isn’t just about adding more licenses; it’s about designing the entire system with growth in mind, ensuring it can adapt to changing needs and emerging technologies.
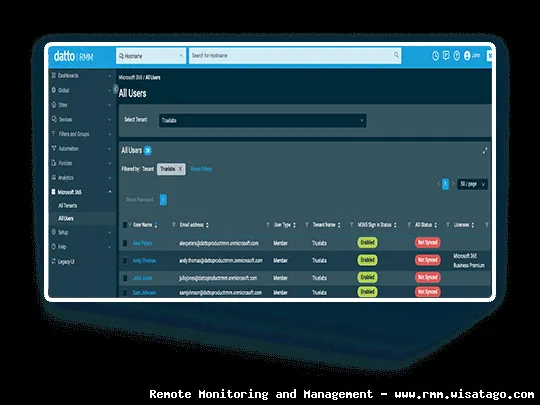
This article will serve as your comprehensive guide to understanding and implementing a scalable RMM architecture for growing enterprises. We’ll delve into the essential features, architectural considerations, and best practices to help you choose and deploy an RMM solution that can keep pace with your company’s growth trajectory. We’ll also explore the challenges you might face and provide practical tips to overcome them. Whether you’re an IT manager, system administrator, or business owner, this guide will equip you with the knowledge you need to make informed decisions about your RMM strategy and ensure your IT infrastructure supports, rather than hinders, your company’s success.
Understanding Scalable RMM Architecture
A scalable RMM architecture is designed to accommodate increasing workloads and data volumes without compromising performance or reliability. It’s not just about adding more servers or licenses; it’s about creating a system that can dynamically adjust to changing demands. This involves several key components working together seamlessly.
Key Components of a Scalable RMM
Here’s a breakdown of the core elements:
- Multi-Tenancy: The ability to manage multiple clients or departments within a single RMM instance. This is crucial for managed service providers (MSPs) but also beneficial for large enterprises with segmented IT environments. Each tenant has its own isolated environment, ensuring data security and privacy.
- Distributed Architecture: Instead of relying on a single, monolithic server, a distributed architecture spreads the workload across multiple servers or cloud instances. This allows for horizontal scaling, meaning you can add more resources as needed without disrupting existing operations.
- Automation and Scripting: Automating routine tasks, such as patch management, software deployment, and system monitoring, is essential for scalability. Scripting capabilities allow you to customize and extend the RMM‘s functionality to meet specific business needs.
- Centralized Management Console: A single pane of glass for managing all aspects of the RMM, including monitoring, alerting, reporting, and remote access. This provides a unified view of the entire IT environment, simplifying administration and troubleshooting.
- Robust Reporting and Analytics: Detailed reports and analytics provide insights into system performance, security vulnerabilities, and potential issues. This allows you to proactively address problems and optimize IT operations.
- API Integration: The ability to integrate with other IT systems, such as ticketing systems, CRM platforms, and security tools, is crucial for streamlining workflows and improving efficiency.
Why Scalability Matters for Growing Enterprises
A non-scalable RMM solution can quickly become a bottleneck, hindering your company’s growth in several ways:
- Increased Downtime: As the number of endpoints and devices increases, a non-scalable RMM may struggle to keep up, leading to performance degradation and increased downtime. This can disrupt business operations and negatively impact productivity.
- Higher Operational Costs: Manually managing a large and complex IT environment is time-consuming and expensive. A scalable RMM automates many routine tasks, reducing the need for manual intervention and lowering operational costs.
- Security Vulnerabilities: A non-scalable RMM may struggle to effectively monitor and protect all endpoints, leaving your company vulnerable to security threats.
- Limited Visibility: Without a centralized management console, it can be difficult to gain a comprehensive view of your IT environment. This makes it harder to identify and resolve problems, leading to inefficiencies and increased risk.
- Inability to Adapt to Change: A non-scalable RMM may not be able to adapt to new technologies or changing business requirements. This can limit your company’s ability to innovate and compete.
Features to Look for in a Scalable RMM Solution
When evaluating RMM solutions for a growing enterprise, it’s crucial to consider the following features:
Agent Management and Deployment
The RMM solution should offer flexible and efficient agent deployment options. This includes:
- Automated Agent Deployment: The ability to automatically deploy agents to new devices without manual intervention.
- Remote Agent Installation: Installing agents remotely on devices without requiring physical access.
- Centralized Agent Management: Managing all agents from a single console, including updating, configuring, and removing agents.
Monitoring and Alerting
Robust monitoring and alerting capabilities are essential for proactive IT management. Look for:
- Real-time Monitoring: Monitoring system performance, network traffic, and application availability in real-time.
- Customizable Alerts: Setting up alerts based on specific thresholds and conditions.
- Alert Escalation: Automatically escalating alerts to the appropriate personnel based on severity and urgency.
- Root Cause Analysis: Tools to help identify the underlying cause of problems and prevent them from recurring.
Patch Management
Automated patch management is crucial for maintaining system security and stability. The RMM should offer:
- Automated Patch Scanning: Automatically scanning for missing patches on all devices.
- Patch Deployment: Deploying patches automatically or manually, based on pre-defined schedules and policies.
- Patch Reporting: Generating reports on patch status and compliance.
- Rollback Capabilities: The ability to rollback patches if they cause problems.
Remote Access and Control
Secure and reliable remote access is essential for troubleshooting and resolving issues remotely. Look for:
- Secure Remote Access: Securely accessing devices remotely using encryption and multi-factor authentication.
- Remote Control: Remotely controlling devices to troubleshoot and resolve issues.
- Background Management: Performing tasks in the background without interrupting the user.
- Session Recording: Recording remote access sessions for auditing and training purposes.
Security Features
Security should be a top priority when choosing an RMM solution. Look for features like:
- Antivirus and Anti-malware Integration: Integration with leading antivirus and anti-malware solutions.
- Firewall Management: Managing firewalls remotely to protect endpoints from unauthorized access.
- Vulnerability Scanning: Scanning for vulnerabilities on endpoints and servers.
- Security Auditing: Auditing security configurations and compliance.
Architectural Considerations for Scalable RMM Deployment
Choosing the right architecture is crucial for ensuring scalability and performance. Here are some key considerations:
Cloud-Based vs. On-Premise RMM
You have two main options: cloud-based RMM and on-premise RMM. Cloud-based RMM solutions are hosted in the cloud and offer several advantages in terms of scalability, cost, and ease of management. On-premise RMM solutions are hosted on your own servers and offer more control over data and security.
- Cloud-Based RMM: Offers automatic scalability, reduced infrastructure costs, and simplified management. However, you’re dependent on the provider’s infrastructure and security.
- On-Premise RMM: Provides more control over data and security but requires more upfront investment and ongoing maintenance. Scalability can be more complex and costly.
Database Design and Optimization
The database is the heart of the RMM solution. Proper database design and optimization are essential for ensuring performance and scalability. Consider:
- Database Choice: Choosing a database that can handle large volumes of data and high transaction rates (e.g., MySQL, PostgreSQL, SQL Server).
- Database Indexing: Properly indexing database tables to improve query performance.
- Database Partitioning: Partitioning the database to distribute data across multiple servers.
- Database Monitoring: Monitoring database performance to identify and resolve bottlenecks.
Network Infrastructure
A robust network infrastructure is essential for reliable RMM operation. Consider:
. Effective IT management often requires specialized tools, and RMM is one such solution that can streamline operations
.
- Bandwidth: Ensuring sufficient bandwidth to handle the traffic generated by the RMM.
- Latency: Minimizing latency between the RMM server and the endpoints.
- Network Security: Implementing security measures to protect the RMM traffic from unauthorized access.
Best Practices for Implementing a Scalable RMM
Follow these best practices to ensure a successful RMM implementation:
Start with a Pilot Project
Before deploying the RMM solution to your entire organization, start with a pilot project involving a small group of users and devices. This allows you to test the solution, identify potential issues, and refine your deployment strategy.
Develop a Comprehensive Training Program
Provide comprehensive training to your IT staff on how to use the RMM solution effectively. This will ensure that they can leverage the RMM‘s capabilities to improve IT operations and security.
Establish Clear Policies and Procedures
Develop clear policies and procedures for using the RMM solution, including guidelines for monitoring, alerting, patch management, and remote access. This will help ensure consistency and compliance.
Regularly Review and Optimize Your RMM Configuration
Regularly review and optimize your RMM configuration to ensure it’s meeting your business needs and providing optimal performance. This includes reviewing alert thresholds, patch management policies, and reporting settings.
Stay Up-to-Date with the Latest RMM Features and Updates
Stay informed about the latest features and updates from your RMM vendor. This will allow you to take advantage of new capabilities and address any known issues.
Challenges and How to Overcome Them
Implementing a scalable RMM solution can present several challenges. Here are some common challenges and how to overcome them:
Data Overload
RMM solutions generate a large amount of data. It’s important to filter and prioritize the data to avoid information overload. Use customizable alerts and reporting to focus on the most critical issues.
Complexity
RMM solutions can be complex to configure and manage. Invest in training and documentation to help your IT staff master the RMM‘s capabilities. Consider hiring a consultant to help with the initial setup and configuration.
Integration Issues
Integrating the RMM solution with other IT systems can be challenging. Ensure that the RMM solution supports the necessary APIs and integrations. Work with your vendors to resolve any integration issues.
Security Risks
RMM solutions can be a target for cyberattacks. Implement strong security measures to protect the RMM server and endpoints. Use multi-factor authentication, encryption, and regular security audits.
Conclusion
A scalable RMM architecture is essential for growing enterprises that need to efficiently manage and protect their increasingly complex IT environments. By carefully considering the features, architectural considerations, and best practices outlined in this guide, you can choose and deploy an RMM solution that can keep pace with your company’s growth and ensure that your IT infrastructure supports your business objectives. Investing in a scalable RMM is not just an IT decision; it’s a strategic investment in your company’s future.
Remember to prioritize security, automation, and integration when selecting an RMM solution. Regularly review and optimize your RMM configuration to ensure it’s meeting your evolving needs. By following these recommendations, you can unlock the full potential of RMM and transform your IT operations from a reactive, fire-fighting mode to a proactive, strategic function that drives business innovation and growth.
Ultimately, the right RMM solution will empower your IT team to proactively manage your IT environment, reduce downtime, improve security, and free up valuable time to focus on strategic initiatives that drive business value. As your company continues to grow, a scalable RMM will be a critical asset in ensuring your IT infrastructure remains a strong foundation for success.

Conclusion
In conclusion, a scalable RMM architecture is no longer a luxury, but a necessity for growing enterprises. We’ve explored the critical components, from robust infrastructure and automated workflows to comprehensive security measures and adaptable reporting, that form the foundation of a resilient and efficient RMM solution. Ignoring these considerations as your organization expands can lead to operational bottlenecks, increased security vulnerabilities, and ultimately, hindered growth. The right RMM architecture empowers IT teams to proactively manage increasingly complex environments, optimize resource allocation, and deliver exceptional service, regardless of scale.
By carefully evaluating your current needs and future projections, and then selecting an RMM platform built for scalability, you can ensure your IT infrastructure remains a strategic asset rather than a liability. We encourage you to assess your existing RMM capabilities against the principles outlined in this article. If you’re ready to take the next step in optimizing your IT management strategy and building a future-proof infrastructure, consider exploring leading RMM solutions and visiting [Your Company Website] to discover how our expertise can help you achieve your business goals.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ) about Scalable RMM Architecture for Growing Enterprises
What are the key architectural considerations when designing a scalable RMM architecture to support the rapid growth of my enterprise, and how can I ensure it avoids performance bottlenecks?
Designing a scalable RMM (Remote Monitoring and Management) architecture for a growing enterprise requires careful consideration of several key factors. First, prioritize a modular design. This allows you to scale individual components (like data collection, alerting, and reporting) independently as needed. Employing a distributed architecture is crucial, distributing workloads across multiple servers or cloud instances to prevent bottlenecks. Consider using a message queue system (e.g., Kafka, RabbitMQ) to decouple components and handle asynchronous tasks efficiently. Effective database design is also paramount. Choose a database capable of handling large volumes of data and consider sharding or partitioning to improve query performance. Finally, implement robust monitoring and alerting systems to proactively identify and address potential performance issues before they impact operations. Regular performance testing under simulated load conditions is vital to identify and resolve bottlenecks proactively.
How can I effectively manage and automate the onboarding of new devices and clients within a scalable RMM solution as my enterprise expands, and what role does automation play in this process?
Efficient device and client onboarding is critical for a scalable RMM solution. Automation is key to streamlining this process as your enterprise grows. Implement automated discovery tools that can identify and register new devices on the network. Use scripting and configuration management tools (e.g., Ansible, Chef, Puppet) to automate the installation of RMM agents and configure them with the appropriate settings. Establish standardized onboarding workflows that can be triggered automatically based on device type or client group. Integrate with your existing IT service management (ITSM) system to automatically create tickets for new device onboarding. Furthermore, leverage APIs to connect your RMM with other systems, such as asset management databases, to ensure accurate and up-to-date information. By automating these tasks, you can significantly reduce the time and effort required to onboard new devices and clients, ensuring consistent configuration and minimizing the risk of errors. Automated policy enforcement ensures all devices adhere to security standards.
What are the best strategies for ensuring data security and compliance within a scalable RMM platform, particularly when dealing with sensitive client data and evolving regulatory requirements?
Data security and compliance are paramount when operating a scalable RMM platform, especially with sensitive client data and evolving regulations like GDPR, HIPAA, and PCI DSS. Implement robust encryption both in transit (using HTTPS) and at rest (encrypting databases and backups). Enforce strict access control policies using role-based access control (RBAC) to limit access to sensitive data based on job function. Regularly audit access logs to detect and investigate suspicious activity. Implement multi-factor authentication (MFA) for all user accounts. Utilize data loss prevention (DLP) tools to prevent sensitive data from leaving the RMM environment. Stay up-to-date with the latest security patches and vulnerabilities. Employ a comprehensive vulnerability management program to identify and remediate security weaknesses. Finally, ensure your RMM platform is compliant with relevant regulations. Conduct regular security audits and penetration testing to validate the effectiveness of your security controls. Regularly review and update your security policies to adapt to evolving threats and compliance requirements.