In the world of managed services, keeping promises is paramount. We, as IT professionals, are essentially selling peace of mind to our clients. A huge part of that peace of mind comes from Service Level Agreements (SLAs). These agreements aren’t just legal documents; they’re the foundation of trust and the yardstick by which our performance is measured. But how do we consistently meet and exceed those SLA expectations, especially when managing hundreds or even thousands of endpoints?
That’s where Remote Monitoring and Management (RMM) platforms come into play. RMM tools have evolved far beyond simple monitoring. They offer a suite of features designed to proactively manage IT infrastructure, automate tasks, and, crucially, track and manage SLAs. Without robust SLA management features within your RMM, you’re essentially flying blind, relying on manual processes and gut feelings to ensure you’re meeting your obligations. This is not only inefficient but also incredibly risky, potentially leading to missed deadlines, unhappy clients, and even financial penalties.

This article will delve into the essential SLA management features within a service provider RMM. We’ll explore how these features can help you define, monitor, and enforce SLAs, ultimately improving service delivery, client satisfaction, and your bottom line. We’ll break down the key functionalities, discuss real-world examples, and explore the challenges and best practices for implementing effective SLA management within your RMM strategy. So, let’s dive in and discover how to leverage your RMM to become an SLA superhero!
Understanding SLAs and Their Importance in Managed Services
Before we jump into the RMM features, let’s quickly recap what SLAs are and why they’re so critical. An SLA is a contract between a service provider (like you) and a client that defines the level of service expected. It typically includes metrics like uptime, response time, resolution time, and specific performance targets. Think of it as a guarantee of quality and availability.
Why are SLAs so Important?
- Sets Expectations: SLAs clearly define what clients can expect from your services, preventing misunderstandings and disputes.
- Provides Accountability: They establish measurable metrics, holding you accountable for delivering the agreed-upon service levels.
- Drives Performance: The need to meet SLA targets motivates your team to proactively manage IT infrastructure and resolve issues quickly.
- Enhances Client Trust: Consistent SLA adherence builds trust and strengthens client relationships.
- Reduces Churn: Satisfied clients are less likely to switch providers, leading to increased customer retention.
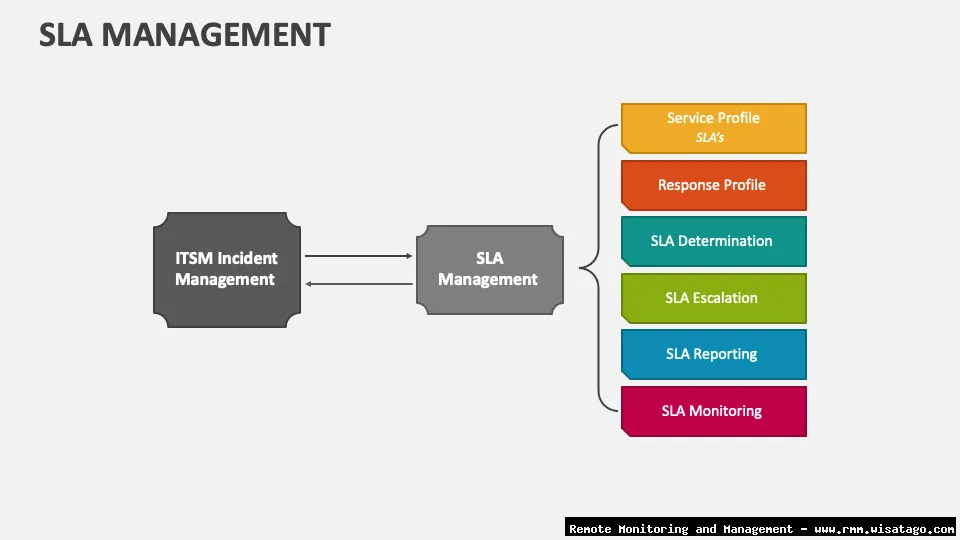
Essential SLA Management Features in RMM Platforms
Now, let’s explore the specific features within an RMM platform that are essential for effective SLA management. These features work together to provide a comprehensive view of your service performance and help you proactively address potential SLA breaches.
Real-time Monitoring and Alerting
This is the foundation of any good SLA management system. The RMM should continuously monitor critical IT infrastructure components (servers, networks, applications, etc.) and generate alerts when performance deviates from defined thresholds. For example, if a server’s CPU utilization exceeds 80% for more than 5 minutes, an alert should be triggered. These alerts need to be configurable to match the specific metrics outlined in your SLAs.

Automated Remediation
While monitoring and alerting are crucial, the real power comes from automated remediation. The RMM should be able to automatically perform pre-defined actions to address common issues and prevent SLA breaches. For instance, if a server runs out of disk space, the RMM could automatically delete temporary files or restart a service. This reduces the need for manual intervention and ensures faster resolution times.
Ticketing System Integration
Seamless integration with your ticketing system is vital. When an alert is triggered, the RMM should automatically create a ticket in your ticketing system, assigning it to the appropriate technician. This ensures that issues are tracked and resolved promptly. The ticket should include all relevant information, such as the affected device, the nature of the problem, and the SLA that is potentially at risk.
SLA-Aware Ticketing
Beyond simple integration, the ticketing system should be “SLA-aware.” This means that the system understands the SLAs associated with each client and prioritizes tickets based on their potential impact on SLA compliance. For example, a ticket related to a critical server outage for a client with a high-priority SLA should be automatically escalated to a senior technician.
Reporting and Analytics
Comprehensive reporting and analytics are essential for tracking SLA performance and identifying areas for improvement. The RMM should provide detailed reports on key metrics like uptime, response time, resolution time, and the number of SLA breaches. These reports should be customizable to meet your specific needs and should allow you to drill down into the data to understand the root causes of SLA violations.
Customizable SLA Definitions
Every client is different, and their SLAs will vary accordingly. Your RMM should allow you to define custom SLAs for each client, specifying the metrics, targets, and penalties for non-compliance. This flexibility is crucial for tailoring your services to meet the unique needs of each client.
Escalation Policies
When issues are not resolved within a certain timeframe, they need to be escalated to higher-level technicians. Your RMM should allow you to define escalation policies that automatically escalate tickets based on pre-defined rules. This ensures that critical issues receive the attention they deserve and that SLA targets are met.
Proactive Patch Management
Keeping systems up-to-date with the latest security patches is crucial for preventing downtime and ensuring SLA compliance. Your RMM should include robust patch management capabilities, allowing you to automatically deploy patches to all managed devices. This reduces the risk of vulnerabilities being exploited and causing service disruptions.
Real-World Use Cases of RMM for SLA Management
Let’s look at some practical examples of how these RMM features can be used to manage SLAs in real-world scenarios.
Use Case 1: Uptime Guarantee
Many managed service providers offer uptime guarantees for their clients’ servers. With an RMM, you can continuously monitor server uptime and receive alerts if a server goes down. The RMM can then automatically restart the server or notify a technician to investigate the issue. The reporting and analytics features can be used to track uptime performance and identify potential issues that could lead to future downtime.
Use Case 2: Response Time Guarantee
Some SLAs specify a maximum response time for resolving support tickets. With RMM integration into your ticketing system, the system can automatically track the time it takes to respond to each ticket and escalate tickets that are approaching the SLA deadline. This ensures that tickets are addressed promptly and that response time targets are met.
Use Case 3: Proactive Problem Prevention
By monitoring system performance and trends, the RMM can identify potential problems before they lead to service disruptions. For example, if a server’s hard drive is filling up, the RMM can alert you to the issue before the server runs out of space and crashes. This proactive approach can help you prevent SLA breaches and maintain high levels of service availability.
Challenges and Best Practices for Implementing RMM-Based SLA Management
While RMM platforms offer powerful tools for managing SLAs, successful implementation requires careful planning and execution. Here are some common challenges and best practices to keep in mind.
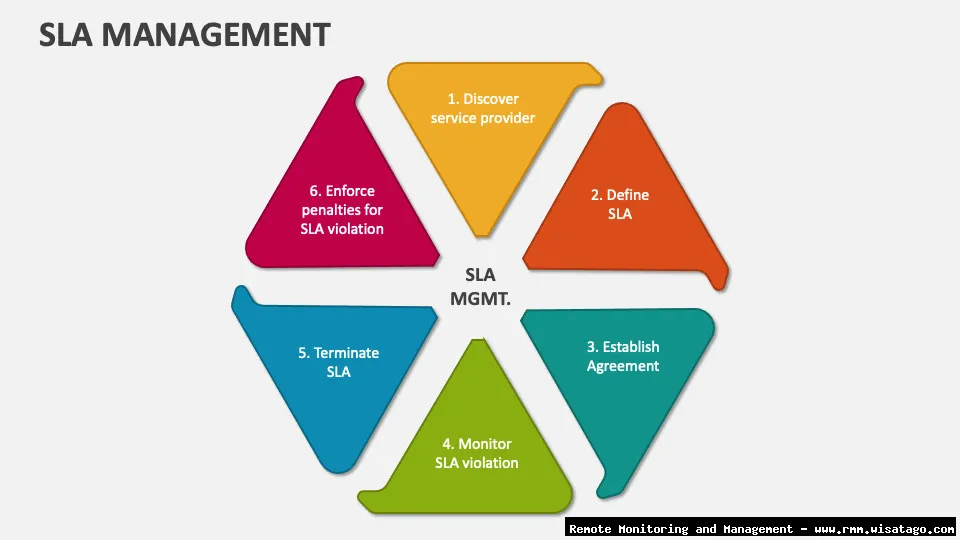
. For more information, you can refer to RMM as an additional resource.
Challenges
- Complexity: RMM platforms can be complex, requiring significant time and effort to configure and maintain.
- Alert Fatigue: If not configured properly, the RMM can generate too many alerts, leading to alert fatigue and missed issues.
- Integration Issues: Integrating the RMM with other systems (e.g., ticketing system, CRM) can be challenging.
- False Positives: Sometimes, alerts are triggered even when there is no actual problem.
Best Practices
- Define Clear SLAs: Ensure that your SLAs are clearly defined and measurable.
- Configure Monitoring Properly: Configure the RMM to monitor the specific metrics that are relevant to your SLAs.
- Tune Alert Thresholds: Adjust alert thresholds to minimize false positives and alert fatigue.
- Automate Remediation: Automate as many remediation tasks as possible to reduce manual intervention.
- Train Your Team: Ensure that your team is properly trained on how to use the RMM platform and manage SLAs.
- Regularly Review and Improve: Continuously review your SLA management processes and look for ways to improve them.
- Document Everything: Maintain detailed documentation of your RMM configuration, SLA definitions, and escalation policies.
Conclusion: Mastering SLAs with Your RMM
Effective SLA management is crucial for the success of any managed service provider. By leveraging the SLA management features within your RMM platform, you can proactively monitor your IT infrastructure, automate remediation tasks, and track SLA performance. This not only helps you meet your obligations to your clients but also improves service delivery, enhances client trust, and ultimately boosts your bottom line. Remember that it’s an ongoing process of refinement and adaptation as your business and your clients’ needs evolve. Investing the time and effort into mastering your RMM‘s SLA management capabilities is an investment in the long-term success of your MSP.
Conclusion
In conclusion, effectively managing Service Level Agreements (SLAs) is paramount for service providers aiming to deliver exceptional IT services and maintain strong client relationships. Integrating robust SLA management features within an RMM platform is no longer a luxury, but a necessity. The ability to track performance against agreed-upon metrics, automate reporting, and proactively address potential breaches ensures service quality, builds trust, and ultimately drives customer satisfaction and retention. By leveraging these capabilities, service providers can transform their RMM solution from a reactive monitoring tool into a proactive service delivery engine.
The insights shared in this article highlight the critical role of SLA management features in optimizing service delivery and bolstering a service provider’s competitive edge. As the demand for reliable and high-performing IT services continues to grow, investing in an RMM solution with comprehensive SLA management capabilities is a strategic imperative. We encourage you to explore the various RMM platforms available and identify the one that best aligns with your specific business needs and client expectations. Consider scheduling a demo with leading RMM vendors to understand firsthand how their SLA management features can empower you to deliver exceptional service and achieve sustainable growth. To learn more about specific features and tools, you can visit our website: example.com/rmm-sla-management.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ) about SLA Management Features in Service Provider RMM
How can a Service Provider’s RMM (Remote Monitoring and Management) platform help me track and enforce Service Level Agreements (SLAs) for my clients?
An RMM platform empowers Service Providers to effectively track and enforce Service Level Agreements (SLAs). It achieves this through several key features. Firstly, it provides real-time monitoring of client systems and networks, allowing for the early detection of potential SLA breaches. This enables proactive intervention before issues impact service delivery. Secondly, RMM tools often include automated alerting systems that notify technicians when performance metrics deviate from agreed-upon SLA targets. This ensures swift responses to critical issues. Thirdly, many RMM platforms offer comprehensive reporting capabilities, allowing Service Providers to generate reports demonstrating SLA compliance and identifying areas for improvement. Finally, some advanced RMM solutions offer automated remediation capabilities. These tools can automatically resolve common issues, minimizing downtime and helping to maintain SLA adherence. By utilizing these features, Service Providers can ensure they are meeting their contractual obligations and providing a high level of service to their clients.
What specific metrics related to network performance and uptime can I monitor within my RMM tool to ensure adherence to my client’s SLA requirements?
To ensure adherence to client SLA requirements, your RMM tool should allow you to monitor several critical metrics related to network performance and uptime. Key metrics include: Uptime percentage, which reflects the total time systems are operational. Response time, measuring the delay between a request and a response, indicating network speed. Packet loss, showing the percentage of data packets that fail to reach their destination, signaling network congestion or instability. Latency, indicating the time it takes for data to travel between two points. Bandwidth utilization, monitoring network capacity usage to prevent bottlenecks. Monitoring CPU utilization, memory usage, and disk space on servers are also vital for ensuring server health and preventing performance degradation which impacts uptime and application performance. By tracking these metrics, Service Providers can proactively identify and address potential issues before they lead to SLA breaches.
How can I generate reports within my Service Provider RMM platform to demonstrate SLA compliance and identify areas where service delivery can be improved for my clients?
Generating reports within your Service Provider RMM platform is crucial for demonstrating SLA compliance and identifying areas for service improvement. Most RMM platforms offer customizable reporting features that allow you to select specific metrics and timeframes. You can generate reports that showcase uptime percentages, response times, and resolution times for incidents. These reports should clearly demonstrate that your service delivery meets or exceeds the agreed-upon SLA targets. Furthermore, utilize reporting to identify recurring issues or trends, such as frequent server outages or slow network performance in specific locations. Analyze these trends to pinpoint areas where proactive maintenance or infrastructure upgrades are needed. Compare performance across different clients to identify best practices and areas where some clients are receiving better service than others. This data-driven approach helps to ensure consistent and high-quality service delivery across your entire client base, ultimately strengthening client relationships.